SCUBA2 Cosmology Legacy Survey
The SCUBA2 Cosmology Legacy Survey (S2CLS) was a collaboration of ~100 scientists across the
three partner countries who ran the James Clerk Maxwell Telescope (JCMT): Canada, the UK and the Netherlands (with a few
individuals based in other countries). The survey exploited the immense increase in mapping speed, fidelity and sensitivity of the SCUBA2 submillimetre camera on the JCMT. The
goal of the survey was to provide the first large
samples of extragalactic sources selected in the 450- and 850-um wavebands. These atmospheric windows allow us to access the redshifted far-infrared emission from luminous but highly, high-redshift galaxies and AGN - pin-pointing an intense era of activity in the early Universe associated with the formation of massive galaxies and black holes.
The survey
has a simple two-tier design, comprising a wide 850-um component and a deeper 450um
survey over a smaller region. The target regions are located in a set of well-defined fields
with appropriately low far-infrared backgrounds, and the extensive multi-frequency
supporting data necessary for our analysis. This single co-ordinated survey programme
aimed to revolutionize our understanding of submillimetre galaxies, and indeed galaxy
formation in general, with enormous and lasting legacy value, as well as providing a
springboard for future exploitation of Atacama Millimeter Array
(ALMA), Herschel, LOFAR, James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and the Square Kilometer Array (SKA).
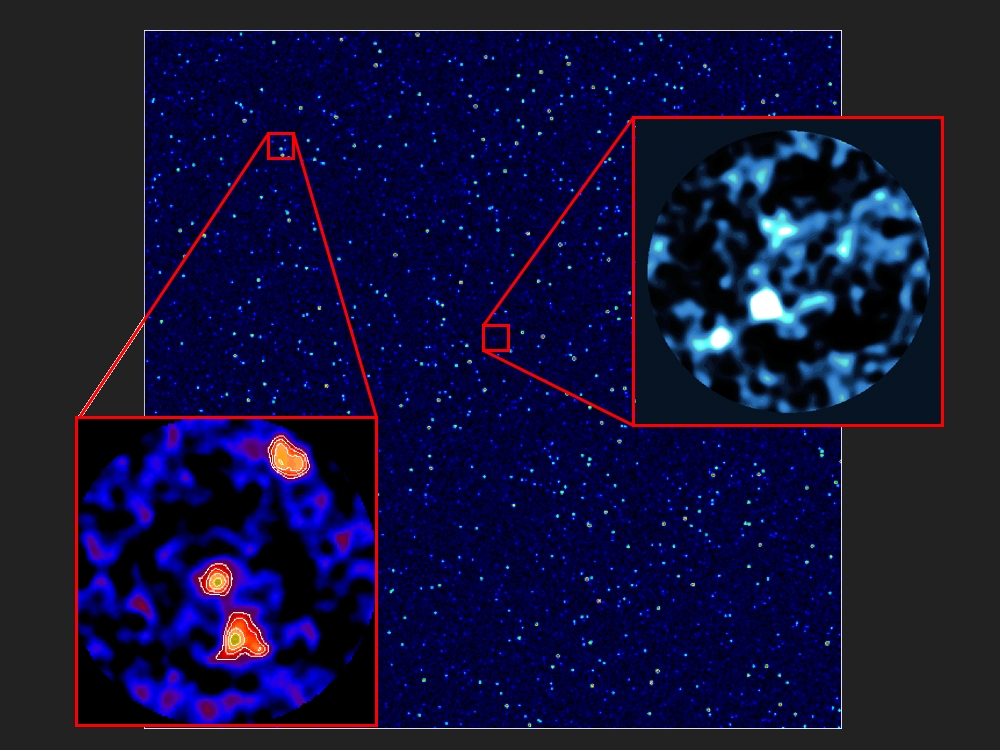
The initial survey design has two elements: 1) a ~1-mJy rms 850um survey of around 35 square degrees, sufficient to map either the accessible Spitzer SWIRE survey regions or other similar-sized regions with comparable supporting data; 2) a deeper survey undertaken in the best conditions to obtain 450-um coverage to 0.5-mJy rms of 1.3 square degrees in the GOODS fields, UKIDSS UDS and COSMOS regions. Owing to observational constraints the original goal areas were reduced by a factor of ~7, resulting in a final survey of ~5 square degrees at 850um and a fraction of square degree at 450um.
The 850um target sensitivity of 1mJy delivered a map in which the noise contributions from the thermal background and extragalactic source confusion noise are comparable. This depth is also sufficient to provide strong (>10-sigma) detections of the ~1,000 bright sources with fluxes >8mJy, essential to i) keep false detections at <1%, ii) provide positions accurate to ~2 arcseconds, to aid in their identifications. These observations also delivered a large number of significant detections at the 3-5 mJy level, allowing the first detailed statistical study of this less-extreme component of the submillimetre galaxy population around the flux limit where the 850um counts exhibit a break in their slope. At the same time they have the area coverage needed to search for rare sub-classes of submillimetre galaxies (e.g. transition objects) which may provide powerful insights into the processes operating within these systems, such as starburst- and AGN-powered feedback, and trace overdensities of submillimetre sources which may pin-point the initial collapse of proto-clusters.
The main driver for the area of the 850-um survey was the need to deliver a sample of sufficient size to reliably measure the clustering of the submillimetre population (to constrain galaxy formation models) and to detect and study the (rare) progenitors of rich clusters. Both of these goals require survey areas of several square degrees. An upper limit to the realistic area of such a survey was provided by the areal coverage of the Spitzer SWIRE fields (see below), which provide the essential supporting multi-wavelength data needed for source identifications, etc. The area of the SWIRE fields accessible from Mauna Kea is approximately 35 square degrees - the goal of the S2CLS was to cover the deepest regions from this area. The allocation of time for this aspect of the survey was eventually sufficient to survey ~5 square degrees (the bulk in the COSMOS and UDS fields).
For the deep 450-um survey, the depth was set by the goal of obtaining the first confusion- limited imaging at 450um (expected to correspond to an rms noise of 0.5mJy). This enable us to resolve for the first time the bulk of the extragalactic background light at 450um, as well as providing precise positions sufficient to directly identify the counterparts to these sources in other wavebands. In parallel with these observations we also obtained extremely deep 850-um observations of these regions which provide both high-quality submillimetre colours for the 450-um sources and information about the very faint 850-um population, although these are highly confused. The atmospheric opacity means that these observations can only sensibly be undertaken in the best conditions and hence the maximum achievable area for the 450-um survey is primarily set by the availability of suitable weather conditions. Nevertheless, the availability of complementary deep, multi-wavelength datasets provided a natural upper limit of ~2 square degrees from the combined area of GOODS-N/S, COSMOS and UKIDSS UDS fields. The 450-um tier of the CLS was the highest ranked element of the entire SCUBA2 legacy programme and so nearly all (almost 90%) of the available Band 1 weather in the first two years of SCUBA2 survey operations was awarded to this survey, totalling 490 hours.
The Cosmology Legacy Survey yielded samples of 1,000's of extragalactic sources with robust detections at 450um or 850um over scales spanning ~30-200Mpc, sufficient to provide fair samples. The survey produced the first reliable measurements of the angular clustering of the 850-um galaxy population, as well as resolving the population responsible for the 450-um extragalactic background. These results and follow-up of the sources from this survey will provide powerful insights into the properties of obscured activity across the history of the Universe. In the longer term, the survey will continue to demonstrate its legacy value through future investigations with ALMA, Herschel and JWST.
More details of the ALMA follow-up of sources selected in the S2CLS fields can be found
The following members of the SCUBA2 Cosmology Legacy Survey are based in Durham: Ian Smail (co-PI), Dave Alexander, Carlton Baugh, Richard Bower, Alastair Edge, Carlos Frenk and Cedric Lacey.
S2CLS papers (and related STUDIES papers) limited to those with significant Durham contributions are listed below:
10) ``Tracing the evolution of dust-obscured activity using sub-millimetre galaxy populations from STUDIES and AS2UDS'', Dudzeviciute, U., Smail, I., Swinbank, A.M., Lim, C.-F., Wang, W.-H., Simpson, J.M., Ao, Y., Chapman, S.C., Chen, C.-C., Clements, D., Dannerbauer, H., Ho, L.C., Hwang, H.S., Koprowski, M., Lee, C.-H., Scott, D., Shim, H., Shirley, R., Toba, Y., 2021, MNRAS, 500, 942-961. PDF version, Abstract [ADS]
9) ``High-resolution imaging with the SMA of bright submillimetre sources from the SCUBA-2 Cosmology Legacy Survey'', Hill, R., Chapman, S.C., Scott, D., Petitpas, G., Smail, I., Chapin, E.L., Gurwell, M.A., Perry, R., Blain, A.W., Bremer, M.N., Chen, C.-C., Dunlop, J.S., Farrah, D., Fazio, G.G., Geach, J.E., Howson, P., Ivison, R.J., Lacaille, K., Michalowski, M.J., Simpson, J.M., Swinbank, A.M., van der Werf, P.P., Wilner, D.J., 2018, MNRAS, 477, 2042-2067. PDF version, Abstract. [ADS]
8) ``SCUBA-2 Ultra Deep Imaging EAO Survey (STUDIES): Faint-end counts at 450um'', Wang, W.-H., Lin, W.-C., Lim, C.-F., Smail, I., Chapman, S.C., Zheng, X., Shim, H., Kodama, T., Almaini, O., Ao, Y., Blain, A.W., Bourne, N., Bunker, A., Chang, Y.-Y., Chao, D., Chen, C.-C., Clements, D., Cowley, W., Dannerbauer, H., Dunlop, J.S., Geach, J.E., Goto, T., Jiang, L., Ivison, R.J., Jeong, W.-S., Kohno, K., Kong, X., Lee, C.-H., Lee, H., Lee, M., Michalowski, M., Oteo, I., Sawicki, M., Scott, D., Shu, X.W., Simpson, J.M., Tee, W.-L., Toba, Y., Valiante, E., Wang, J.-X., Wang, R., Wardlow, J.L., 2017, ApJ, 850, 37-53. PDF version, Abstract. [ADS]
7) ``An imperfectly passive nature: Bright sub-millimeter emission from dust-obscured star formation in the z=3.717 "passive" system, ZF20115'', Simpson, J.M., Smail, I., Wang, W.-H., Riechers, D., Dunlop, J.S., Ao, Y., Bourne, N., Bunker, A., Chapman, S.C., Chen, C.-C., Dannerbauer, H., Geach, J.E., Goto, T., Harrison, C.M., Hwang, H.S., Ivison, R.J., Kodama, T., Lee, C.-H., Lee, H.-M., Lee, M., Lim, C.-F., Michalowski, M.J., Rosario, D.J., Shim, H., Shu, X.W., Swinbank, A.M., Tee, W.-L., Toba, Y., Valiante, E., Wang, J., Zheng, X.Z., 2017, ApJ, 844, L10-L14. PDF version, Abstract. [ADS]
6) ``The SCUBA-2 Cosmology Legacy Survey: 850um maps, catalogues and number counts'', Geach, J.E., Dunlop, J.S., Halpern, M., Smail, I., van der Werf, P., Alexander, D.M., Almaini, O., Aretxaga, I., Arumugam, V., Asboth, V., Banerji, M., Beanlands, J., Best, P.N., Blain, A.W., Birkinshaw, M., Chapin, E.L., Chapman, S.C., Chen, C.-C., Chrysostomou, A., Clarke, C., Clements, D.L., Conselice, C., Coppin, K.E.K., Cowley, W.I., Danielson, A.L.R., Eales, S.A., Edge, A.C., Farrah, D., Gibb, A., Harrison, C.M., Hine, N.K., Hughes, D., Ivison, R.J., Jarvis, M., Jenness, T., Jones, S. F., Karim, A., Koprowski, M., Knudsen, K.K., Lacey, C.G., Mackenzie, T., Marsden, G., McAlpine, K., McMahon, R., Meijerink, R., Michalowski, M.J., Oliver, S.J., Page, M.J., Peacock, J.A., Rigopoulou, D., Robson, E.I., Roseboom, I., Rotermund, K., Scott, D., Serjeant, S., Simpson, C.J., Simpson, J.M., Smith, D.J.B., Spaans, M., Stanley, F., Stevens, J.A., Swinbank, A.M., Targett, T., Thomson, A.P., Valiante, E., Webb, T.M.A., Willott, C., Zavala, J.A., Zemcov, M., 2017, MNRAS, 465, 1789-1806. PDF version, Abstract. [ADS]
5) ``The SCUBA-2 Cosmology Legacy Survey: The clustering of submillimetre galaxies in the UKIDSS UDS field'', Wilkinson, A., Almaini, O., Chen, C.-C., Smail, I., Arumugam, V., Blain, A.W., Chapin, E.L., Chapman, S.C., Conselice, C.J., Cowley, W.I., Dunlop, J.S., Farrah, D., Geach, J.E., Hartley, W.G., Ivison, R.J., Maltby, D.T., Michalowski, M.J., Mortlock, A., Scott, D., Simpson, C.J., Simpson, J.M., van der Werf, P., Wild, V., 2017, MNRAS, 464, 1380-1392. PDF version, Abstract. [ADS]
4) ``The SCUBA-2 Cosmology Legacy Survey: Multi-wavelength counterparts to 103 submillimeter galaxies in UKIDSS-UDS'', Chen, C.C., Smail, I., Ivison, R.J., Arumugam, V., Almaini, O., Ma, C.-J., Swinbank, A.M., Wilkinson, A., Aretzaga, I., Blain, A.W., Chapman, S.C., Conselice, C.J., Dunlop, J.S., Farrah, D., Halpern, M., Hartley, W.G., Michalowski, M.J., Mortlock, A., Simpson, C.J., Simpson, J.M., van der Werf, P., Zavala, J., 2016, ApJ, 820, 82. PDF version, Abstract. [ADS]
3) ``The SCUBA-2 Cosmology Legacy Survey: Ultraluminous star-forming galaxies in a z=1.6 cluster'', Smail, I., Geach, J.E., Swinbank, A.M., Tadaki, K., Arumugam, V., Hartley, W., Almaini, O., Bremer, M.N., Chapin, E., Chapman, S.C., Danielson, A.L.R., Edge, A.C., Scott, D., Simpson, C.J., Simpson, J.M., Conselice, C., Dunlop, J.S., Ivison, R.J., Karim, A., Kodama, T., Mortlock, A., Robson, E.I., Roseboom, I., Thomson, A.P., van der Werf, P.P., Webb, T.M.A., 2014, ApJ, 782, 19-34. PDF version, Abstract. [ADS]
2) ``The SCUBA-2 Cosmology Legacy Survey: Demographics of the 450um population'', Roseboom, I.G., Dunlop, J.S., Cirasuolo, M., Geach, J.E., Smail, I., Halpern, M., van der Werf, P., Almaini, O., Arumugam, V., Asboth, V., Auld, R., Blain, A., Bremer, M., Bock, J., Bowler, R., Buitrago, F., Chapin, E., Chapman, S., Chrysostomou, A., Clarke, C., Conley, A., Coppin, K.E.K., Danielson, A., Farrah, D., Glenn, J., Hatziminaoglou, E., Ibar, E., Ivison, R.J., Jenness, T., van Kampen, E., Karim, A., Mackenzie, T., Marsden, G., Meijerink, R., Michalowski, M.J., Oliver, S.J., Page, M.J., Pearson, E., Scott, D., Simpson, J., Spaans, M., Symeonidis, M., Smith, D.J.B., Swinbank, A.M., Targett, T., Valiante, E., Viero, M., Wang, L., Willott, C.J., Zemcov, M., 2013, MNRAS, 436, 430-448. PDF version, Abstract. [ADS]
1) ``The SCUBA-2 Cosmology Legacy Survey: blank-field number counts of 450um-selected galaxies and their contribution to the cosmic infrared background'', Geach, J.E., Chapin, E.L., Coppin, K.E.K., Dunlop, J.S., Halpern, M., Smail, I., van der Werf, P., Serjeant, S., Farrah, D., Roseboom, I., Targett, T., Arumugam, V., Asboth, V., Blain, A.W., Chrysostomou, A., Clark, C., Ivison, R.J., Jones, S.L., Karim, A., Mackenzie, T., Meijerink, R., Michalowski, M.J., Scott, D., Simpson, J., Swinbank, A.M., Alexander, D., Almaini, O., Aretxaga, I., Best, P.N., Chapman, S.C., Clements, D.L., Conselice, C., Danielson, A.L.R., Eales, S., Edge, A.C., Gibb, A., Hughes, D.H., Jenness, T., Knudsen, K.K., Lacey, C., Marsden, G., McMahon, R., Oliver, S., Page, M.J., Peacock, J.A., Rigopoulou, D., Robson, E.I., Spaans, M., Stevens, J.A., Webb, T.M.A., Willott, C., Wilson, C., Zemcov, M., 2013, MNRAS, 432, 53-61. PDF version, Abstract. [ADS]